Startup funding: Bootstrapping vs Venture capital
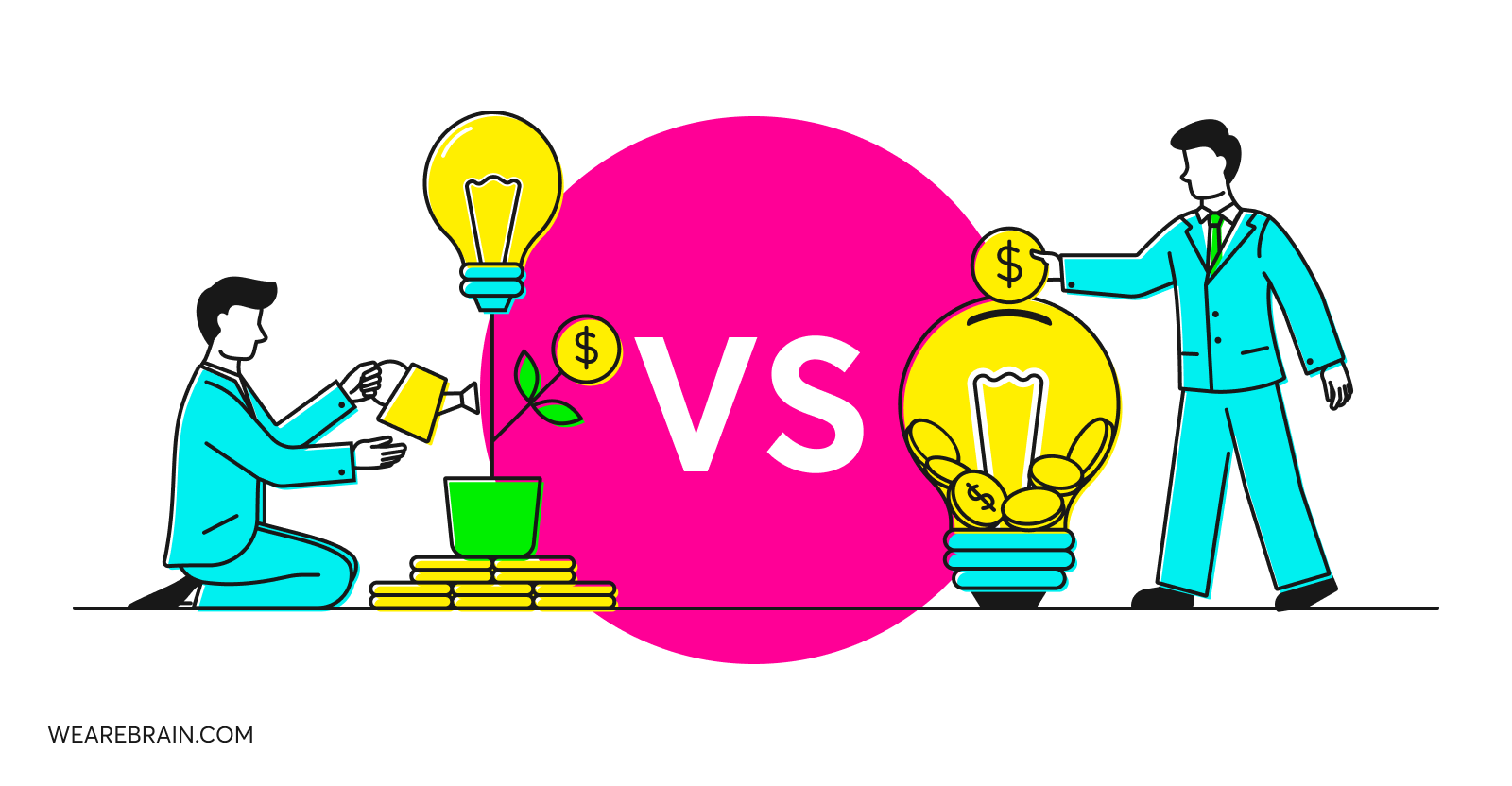
One of the most crucial early-stage decisions entrepreneurs face is how to fund their venture. Ideas remain only ideas if you’re unable to fund their development. So, once the ideation frenzy has settled, entrepreneurs are left with two primary avenues to fund their projects: bootstrapping or venture capital.
Each comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, making the choice between them a pivotal moment in a startup’s journey.
As entrepreneurs ourselves, having assisted a number of successful startups in becoming industry titans, we’ve learned a thing or two about the entrepreneurial adventure along the way. Here’s a beginner’s guide on how to go about your startup funding journey.
Bootstrapping vs Venture capital: What’s the difference?
Before diving into the depths of startup funding, let’s establish a clear understanding of bootstrapping and venture capital.
Bootstrapping involves self-funding a business, relying on personal savings or revenue generated by the business itself. On the other hand, venture capital entails raising funds from external investors in exchange for equity in the business.
The significance of choosing the right funding strategy cannot be overstated. It shapes the trajectory of your startup, influencing everything from your level of control to your growth potential and ultimate success. So, it is essential for entrepreneurs and startup founders to deeply understand what each funding approach entails and its future impact on the business.
Advantages of bootstrap funding
Let’s take a look at how bootstrapping your startup funding can provide you with numerous benefits:
Full control
One of the most enticing aspects of bootstrapping is the autonomy it offers entrepreneurs. With no external investors to answer to, founders have full control over decision-making processes, enabling them to steer the company in line with their vision.
Limited debt
Bootstrapping eliminates the burden of debt that often comes with external financing. Without owing money to investors or lenders, startups can operate with greater financial flexibility and focus on building a sustainable business model.
Profit orientation
Bootstrapped startups are inherently profit-oriented. With limited resources at their disposal, entrepreneurs are incentivised to prioritise revenue generation and profitability from the outset, fostering a lean and efficient operation.
Challenges of bootstrap funding
While the benefits of full autonomy, reduced debt, and an immediate orientation towards profit are alluring, there are some drawbacks to bootstrapping to be aware of:
Limited resources
Bootstrapping often means operating within tight budget constraints, which can hinder growth opportunities. Without access to substantial capital, startups may struggle to invest in scaling initiatives or seize market opportunities.
Slow growth
While bootstrapping encourages financial responsibility, it can also result in slower growth compared to ventures backed by external funding. The trade-off between steady, organic growth and rapid expansion with substantial investments is a common dilemma for bootstrapped startups.
Personal stress
The financial risk inherent in bootstrapping can take a toll on founders’ mental well-being. The constant pressure to make ends meet and ensure the company’s survival can lead to heightened levels of stress and anxiety.
Advantages of venture capital funding
If bootstrapping doesn’t feel like the right for your startup funding initiatives, then another great alternative is available. There are numerous advantages of going the venture capital route, including:
Rapid growth
Venture capital has the potential to fuel rapid growth and scale at an accelerated pace. With access to substantial financial resources, startups can invest in scaling initiatives, expand their operations, and capture market share more aggressively.
Less personal risk
Unlike bootstrapping, venture capital mitigates the personal financial risk for founders. Since the funding comes from external investors, entrepreneurs are not personally liable for any losses incurred by the business. This has a positive impact on the well-being of entrepreneurs who can focus on making the company work without battling the stresses that come with personal investment.
Access to expertise and connections
Venture capitalists bring more than just capital to the table – they offer invaluable expertise, industry insights, and strategic guidance. Additionally, their extensive networks can open doors to potential partnerships, customers, and talent. This exposes the startup to networks they might never have been able to reach if they were to bootstrap.
Challenges of venture capital funding
Understanding the benefits of venture capital funding might initially appear to be the right fit for your business. However, some inherent challenges come with it. These can include:
Loss of control
Accepting venture capital inevitably entails handing over a degree of control of the company. Investors often have a say in major decisions, and founders may find themselves navigating competing interests and priorities.
Intense competition
Securing venture capital is a highly competitive process, with only a fraction of startups able to successfully raise the required funding. Standing out requires a compelling value proposition, a solid business plan, and exceptional execution capabilities.
Pressure to exit
Venture capitalists typically have a small investment scope and expect a substantial return on their investment within a specified timeframe. This can add pressure on founders to prioritise short-term gains and pursue exit opportunities, potentially at the expense of long-term value creation.
How to choose: bootstrapping or venture capital?
So, how do you decide which option is the most viable for your startup? Well, there are a few critical components to be aware of when making this important business decision. After all, the pros and cons of bootstrapping vs venture capital will likely depend on your business type, goals, and objectives.
Here’s a 6-step process to help you understand which route is best for your startup:
1. Assess your business goals
Begin by clearly defining your startup’s short-term and long-term objectives. Consider whether rapid growth and market domination align with your vision or if a more conservative approach focused on profitability and sustainability is preferable.
2. Evaluate your financial resource needs
Conduct a thorough analysis of your financial requirements for product development, marketing, and operational expenses. Determine whether bootstrapping can adequately meet these needs or if external funding is essential for scaling.
3. Consider control and ownership
Evaluate the level of control and ownership you’re willing to give up in exchange for external funding. While bootstrapping affords you autonomy, venture capital offers access to expertise and networks but comes with strings attached.
4. Understand your risk tolerance
Assess your risk tolerance and willingness to share control of your startup. Consider how comfortable you are with shouldering the financial risk associated with bootstrapping versus the potential loss of autonomy with venture capital.
5. Asses market conditions
Take stock of the current market landscape and competitive dynamics in your chosen industry. Assess the availability of capital, investor sentiment, and industry trends to gauge the feasibility of each funding option.
6. Have an exit strategy
Evaluate the implications of each funding method on potential exit strategies for your business. Consider whether you envision a lucrative acquisition, an initial public offering (IPO), or other avenues for realising returns for yourself and your investors. Understanding this will help you be proactive rather than reactive to the fluctuations of a new business.
Ready, set, go!
The choice between bootstrapping and venture capital is a pivotal decision for entrepreneurs as it fundamentally dictates the future of your startup. Both paths offer distinct advantages and challenges, and the decision hinges on factors such as your business goals, financial needs, risk tolerance, and market conditions.
By carefully weighing these considerations and aligning them with your startup’s unique characteristics and aspirations, you can make an informed decision that sets the stage for success.
Remember, the journey of entrepreneurship is as much about the decisions you make as it is about the journey itself. Choose wisely, and may your startup thrive amidst the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Looking to cut SaaS costs? Download our SaaS Cost Reduction Checklist for expert tips on optimizing your stack and saving money👇
Enter your email to download the SaaS costs reduction checklist instantly.
By filling out your email address you consent to receive WeAreBrain’s newsletter with its latest news. WeAreBrain does not share or sell your personal information.
Elvire Jaspers
Working Machines
An executive’s guide to AI and Intelligent Automation. Working Machines takes a look at how the renewed vigour for the development of Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Automation technology has begun to change how businesses operate.